# FreeRTOS 内存分配选择
在 FreeRTOS 中,可以用静态(不使用 FreeRTOS 堆)或动态来分配 RTOS 的对象; 因此 FreeRTOS 中提供了 5 种堆管理方案,这些方案的复杂性和功能使得它的使用范围广泛,当然用户也可以自己实现堆管理;在官方的例程中,动静态的使用选择可以通过使能宏 configSUPPORT_STATIC_ALLOCATION 和宏 configSUPPORT_DYNAMIC_ALLOCATION 来进行决定(官方默认是使用动态内存进行分配的),当然,前提是使用 FreeRTOS 提供的 heap 堆分配的其中一个文件,而不是用自己实现的堆管理;甚至你还可以两种方法都在同一 RTOS 应用程序中使用。
# 静态与动态内存分配
V9.0.0 之前的 FreeRTOS 版本是从特殊的 FreeRTOS 堆中(也就是这几个 heap 文件)分配下面列出的 RTOS 对象使用的内存。而在 FreeRTOS V9.0.0 及更高版本中,人们可以自己实现堆管理提供内存,从而可以选择创建以下对象,而无需动态分配任何内存:
- 任务
- 软件计时器
- 队列
- 事件
- 二值信号量
- 计数信号量
- 递归信号量
- 互斥量
1、使用动态分配的 RAM 创建 RTOS 对象
动态创建 RTOS 对象的好处是可以更加简单、并有可能尽最大程度地减少应用程序的最大 RAM 使用量
如果 configSUPPORT_DYNAMIC_ALLOCATION 设置为 1 或未定义,以下 API 函数将使用动态分配的 RAM 创建 RTOS 对象:
- xTaskCreate()
- xQueueCreate()
- xTimerCreate()
- xEventGroupCreate()
- xSemaphoreCreateBinary()
- xSemaphoreCreateCounting()
- xSemaphoreCreateMutex()
- xSemaphoreCreateRecursiveMutex()
2、使用静态分配的 RAM 创建 RTOS 对象
使用静态分配的 RAM 创建 RTOS 对象的好处是为应用程序编写者提供了更多控制权
下列 API 函数(如果 configSUPPORT_STATIC_ALLOCATION 设置为 1 时可用)允许使用应用程序编写者实现的堆管理创建 RTOS 对象。为了提供内存,应用程序编写者只需要声明一个适当对象类型的变量,然后将变量的地址传递给 RTOS API 函数即可。官方也提供了 StaticAllocation.c 标准的演示 / 测试任务来演示如何使用这些功能:
- xTaskCreateStatic()
- xQueueCreateStatic()
- xTimerCreateStatic()
- xEventGroupCreateStatic()
- xSemaphoreCreateBinaryStatic()
- xSemaphoreCreateCountingStatic()
- xSemaphoreCreateMutexStatic()
- xSemaphoreCreateRecursiveMutexStatic()
# 内存管理
如果 RTOS 对象是动态创建的,则有时可以使用标准 C 库 malloc() 和 free() 函数来实现此目的,但是 …
- 它们并不总是在嵌入式系统上可用;
- 他们占用了宝贵的代码空间;
- 它们不是线程安全的;
- 它们不是确定性的(执行函数所花费的时间因调用而异)。
因此,通常需要另一种内存分配实现。
一个嵌入式 / 实时系统可能具有与另一个系统不同的 RAM 和时序要求;因此,单个 RAM 分配算法仅适用于部分应用程序。
为了解决这个问题,FreeRTOS 将内存分配 API 保留在其可移植层中;当 RTOS 内核需要 RAM 时,它不调用 malloc() ,而是调用 pvPortMalloc() ;当释放 RAM 时,RTOS 内核将调用 vPortFree() 而不是调用 free() 。
在 FreeRTOSv9.0.0\FreeRTOS\Source\portable\MemMang 文档中,FreeRTOS 提供了五个内存分配实现:
- heap_1 – 最简单,不允许释放内存。
- heap_2 – 允许释放内存,但不合并相邻的空闲块。
- heap_3 – 简单包装标准
malloc()和free()以确保线程安全。 - heap_4 – 合并相邻的空闲块以避免碎片;包括绝对地址放置选项。
- heap_5 – 参照
heap_4,能够跨多个不相邻的内存区域扩展堆。
# heap_1.c
在这个文件中有这么一项注释: The simplest possible implementation of pvPortMalloc(). Note that this implementation does NOT allow allocated memory to be freed again. 也就是表明了 heap_1.c 这个文件的功能只能进行分配,不支持释放内存。
它的分配函数实现:
void *pvPortMalloc( size_t xWantedSize ) | |
{ | |
void *pvReturn = NULL; | |
static uint8_t *pucAlignedHeap = NULL; | |
/* Ensure that blocks are always aligned to the required number of bytes. */ | |
#if( portBYTE_ALIGNMENT != 1 ) | |
{ | |
if( xWantedSize & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) | |
{ | |
/* Byte alignment required. */ | |
xWantedSize += ( portBYTE_ALIGNMENT - ( xWantedSize & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) ); | |
} | |
} | |
#endif | |
vTaskSuspendAll(); | |
{ | |
if( pucAlignedHeap == NULL ) | |
{ | |
/* Ensure the heap starts on a correctly aligned boundary. */ | |
pucAlignedHeap = ( uint8_t * ) ( ( ( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE ) &ucHeap[ portBYTE_ALIGNMENT ] ) & ( ~( ( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE ) portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) ) ); | |
} | |
/* Check there is enough room left for the allocation. */ | |
if( ( ( xNextFreeByte + xWantedSize ) < configADJUSTED_HEAP_SIZE ) && | |
( ( xNextFreeByte + xWantedSize ) > xNextFreeByte ) )/* Check for overflow. */ | |
{ | |
/* Return the next free byte then increment the index past this | |
block. */ | |
pvReturn = pucAlignedHeap + xNextFreeByte; | |
xNextFreeByte += xWantedSize; | |
} | |
traceMALLOC( pvReturn, xWantedSize ); | |
} | |
( void ) xTaskResumeAll(); | |
#if( configUSE_MALLOC_FAILED_HOOK == 1 ) | |
{ | |
if( pvReturn == NULL ) | |
{ | |
extern void vApplicationMallocFailedHook( void ); | |
vApplicationMallocFailedHook(); | |
} | |
} | |
#endif | |
return pvReturn; | |
} |
既然这么简单,就稍微分析一下吧!
1、首先是对内存对齐的判断,这里,如果内存对齐有效,则执行;如果要分配的内存不是对齐字节 (通常是 8,根据 portBYTE_ALIGNMENT 来确定对齐字节) 的整数倍,则补齐,所以 xWantedSize 要加上要补齐的长度。
/* Ensure that blocks are always aligned to the required number of bytes. */ | |
#if( portBYTE_ALIGNMENT != 1 ) | |
{ | |
if( xWantedSize & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) | |
{ | |
/* Byte alignment required. */ | |
xWantedSize += ( portBYTE_ALIGNMENT - ( xWantedSize & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) ); | |
} | |
} | |
#endif |
2、接着挂起所有的调度器,防止在分配内存的过程中被打断。
vTaskSuspendAll(); |
3、判断是否为第一次分配,若是,则检查初分配的内存是否有对齐,这里 uheap 是一个静态数组(是 FreeRTOS 为我们申请的一个内存堆,大小由宏 configTOTAL_HEAP_SIZE 决定),首先要确保它是否对齐,因为 uheap 的首地址可能不是 8 的倍数,若是没有对齐,那么进行对齐处理,以确保实际开始分配的地址是对齐的,值得留意的是,这个对齐处理只做一次。
if( pucAlignedHeap == NULL ) | |
{ | |
/* Ensure the heap starts on a correctly aligned boundary. */ | |
pucAlignedHeap = ( uint8_t * ) ( ( ( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE ) &ucHeap[ portBYTE_ALIGNMENT ] ) & ( ~( ( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE ) portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) ) ); | |
} |
4、在正式分配前进行溢出检查,如果空间够用,则记录新分配空间的首地址到 pvReturn ,并重新记录新的空闲空间的首地址到 NextFreeByte 。
/* Check there is enough room left for the allocation. */ | |
if( ( ( xNextFreeByte + xWantedSize ) < configADJUSTED_HEAP_SIZE ) && | |
( ( xNextFreeByte + xWantedSize ) > xNextFreeByte ) )/* Check for overflow. */ | |
{ | |
/* Return the next free byte then increment the index past this block. */ | |
pvReturn = pucAlignedHeap + xNextFreeByte; | |
xNextFreeByte += xWantedSize; | |
} |
5、 traceMALLOC( pvReturn, xWantedSize ) 是一个宏,用于输出内存分配的调试信息,这个宏定义在 FreeRTOS.h 中,默认为空,如果需要将这些调试信息输出到串口或其它东西,就可以修改这个宏将信息输出到所需要的地方。
traceMALLOC( pvReturn, xWantedSize ); |
6、最后,恢复之前挂起的调度器
( void ) xTaskResumeAll(); |
7、这个取决于宏 configUSE_MALLOC_FAILED_HOOK 是否使能,如果开启了分配失败 hook 函数,就调用该 hook 。
#if( configUSE_MALLOC_FAILED_HOOK == 1 ) | |
{ | |
if( pvReturn == NULL ) | |
{ | |
extern void vApplicationMallocFailedHook( void ); | |
vApplicationMallocFailedHook(); | |
} | |
} | |
#endif |
适用环境以及功能简介:
- 如果您的应用程序从不删除任务,队列,信号量,互斥锁等,则可以使用它(实际上涵盖了使用 FreeRTOS 的大多数应用程序)。
- 始终是确定性的(总是花费相同的时间来执行),并且不会导致内存碎片。
- 它是非常简单的,可以从静态分配的数组中分配内存,这意味着它通常适用于不允许真正的动态内存分配的应用程序。
# heap_2.c
此方案使用了最佳适应算法(best fit algorithm),并且与方案 1 不同,它允许释放以前分配的块;它不会将相邻的空闲块合并成一个大块。
同样的,文件里的注释: A sample implementation of pvPortMalloc() and vPortFree() that permits allocated blocks to be freed, but does not combine adjacent free blocks into a single larger block (and so will fragment memory). 也就是说现在支持分配和释放内存,但对内存碎片不做处理。
1、在实现堆分配之前,有一个堆初始化的过程 prvHeapInit() ,并且只调用一次(就是第一次进入该函数的时候)
static void prvHeapInit( void ) | |
{ | |
BlockLink_t *pxFirstFreeBlock; | |
uint8_t *pucAlignedHeap; | |
/* Ensure the heap starts on a correctly aligned boundary. */ | |
pucAlignedHeap = ( uint8_t * ) ( ( ( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE ) &ucHeap[ portBYTE_ALIGNMENT ] ) & ( ~( ( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE ) portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) ) ); | |
/* xStart is used to hold a pointer to the first item in the list of free | |
blocks. The void cast is used to prevent compiler warnings. */ | |
xStart.pxNextFreeBlock = ( void * ) pucAlignedHeap; | |
xStart.xBlockSize = ( size_t ) 0; | |
/* xEnd is used to mark the end of the list of free blocks. */ | |
xEnd.xBlockSize = configADJUSTED_HEAP_SIZE; | |
xEnd.pxNextFreeBlock = NULL; | |
/* To start with there is a single free block that is sized to take up the | |
entire heap space. */ | |
pxFirstFreeBlock = ( void * ) pucAlignedHeap; | |
pxFirstFreeBlock->xBlockSize = configADJUSTED_HEAP_SIZE; | |
pxFirstFreeBlock->pxNextFreeBlock = &xEnd; | |
} |
这里用到了 BlockLink_t 结构体,这个结构有两个成员,第一个是节点 Next 指针 pxNextFreeBlock ,第二个是空闲块大小。结构体成员如下:
/* Define the linked list structure. This is used to link free blocks in order | |
of their size. */ | |
typedef struct A_BLOCK_LINK | |
{ | |
struct A_BLOCK_LINK *pxNextFreeBlock; /*<< The next free block in the list. */ | |
size_t xBlockSize; /*<< The size of the free block. */ | |
} BlockLink_t; |
首先,对开辟的堆进行地址对齐工作,对齐的原因的原理与 heap_1 一样,在获取堆的首地址后,对 xStart 链表头和 xEnd 链表尾进行初始化赋值;在 heap_2 中,与 heap_1 不同的是,由于 FreeRTOS 用空闲块对内存堆进行管理,于是用 BlockLink_t 这一个结构来形成一条空闲块链表对空闲块进行组织和管理。
2、好了,现在回到 pvPortMalloc() 函数中。
void *pvPortMalloc( size_t xWantedSize ) | |
{ | |
BlockLink_t *pxBlock, *pxPreviousBlock, *pxNewBlockLink; | |
static BaseType_t xHeapHasBeenInitialised = pdFALSE; | |
void *pvReturn = NULL; | |
vTaskSuspendAll(); | |
{ | |
/* If this is the first call to malloc then the heap will require | |
initialisation to setup the list of free blocks. */ | |
if( xHeapHasBeenInitialised == pdFALSE ) | |
{ | |
prvHeapInit(); | |
xHeapHasBeenInitialised = pdTRUE; | |
} | |
/* The wanted size is increased so it can contain a BlockLink_t | |
structure in addition to the requested amount of bytes. */ | |
if( xWantedSize > 0 ) | |
{ | |
xWantedSize += heapSTRUCT_SIZE; | |
/* Ensure that blocks are always aligned to the required number of bytes. */ | |
if( ( xWantedSize & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) != 0 ) | |
{ | |
/* Byte alignment required. */ | |
xWantedSize += ( portBYTE_ALIGNMENT - ( xWantedSize & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) ); | |
} | |
} | |
if( ( xWantedSize > 0 ) && ( xWantedSize < configADJUSTED_HEAP_SIZE ) ) | |
{ | |
/* Blocks are stored in byte order - traverse the list from the start | |
(smallest) block until one of adequate size is found. */ | |
pxPreviousBlock = &xStart; | |
pxBlock = xStart.pxNextFreeBlock; | |
while( ( pxBlock->xBlockSize < xWantedSize ) && ( pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock != NULL ) ) | |
{ | |
pxPreviousBlock = pxBlock; | |
pxBlock = pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock; | |
} | |
/* If we found the end marker then a block of adequate size was not found. */ | |
if( pxBlock != &xEnd ) | |
{ | |
/* Return the memory space - jumping over the BlockLink_t structure | |
at its start. */ | |
pvReturn = ( void * ) ( ( ( uint8_t * ) pxPreviousBlock->pxNextFreeBlock ) + heapSTRUCT_SIZE ); | |
/* This block is being returned for use so must be taken out of the | |
list of free blocks. */ | |
pxPreviousBlock->pxNextFreeBlock = pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock; | |
/* If the block is larger than required it can be split into two. */ | |
if( ( pxBlock->xBlockSize - xWantedSize ) > heapMINIMUM_BLOCK_SIZE ) | |
{ | |
/* This block is to be split into two. Create a new block | |
following the number of bytes requested. The void cast is | |
used to prevent byte alignment warnings from the compiler. */ | |
pxNewBlockLink = ( void * ) ( ( ( uint8_t * ) pxBlock ) + xWantedSize ); | |
/* Calculate the sizes of two blocks split from the single | |
block. */ | |
pxNewBlockLink->xBlockSize = pxBlock->xBlockSize - xWantedSize; | |
pxBlock->xBlockSize = xWantedSize; | |
/* Insert the new block into the list of free blocks. */ | |
prvInsertBlockIntoFreeList( ( pxNewBlockLink ) ); | |
} | |
xFreeBytesRemaining -= pxBlock->xBlockSize; | |
} | |
} | |
traceMALLOC( pvReturn, xWantedSize ); | |
} | |
( void ) xTaskResumeAll(); | |
#if( configUSE_MALLOC_FAILED_HOOK == 1 ) | |
{ | |
if( pvReturn == NULL ) | |
{ | |
extern void vApplicationMallocFailedHook( void ); | |
vApplicationMallocFailedHook(); | |
} | |
} | |
#endif | |
return pvReturn; | |
} |
同样的,在每次分配空间之前,先挂起调度器,这是没得说的,然后如果是第一次调用 pvPortMalloc() ,则调用 prvHeapInit() 对内存堆和空闲块链表进行初始化;而下面这段 code:
/* The wanted size is increased so it can contain a BlockLink_t | |
structure in addition to the requested amount of bytes. */ | |
if( xWantedSize > 0 ) | |
{ | |
xWantedSize += heapSTRUCT_SIZE; | |
/* Ensure that blocks are always aligned to the required number of bytes. */ | |
if( ( xWantedSize & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) != 0 ) | |
{ | |
/* Byte alignment required. */ | |
xWantedSize += ( portBYTE_ALIGNMENT - ( xWantedSize & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) ); | |
} | |
} |
在用户每申请一次内存,FreeRTOS 都会在申请的空间前加上空闲块头部 BlockLink_t ,用于记录分配出去的空间的大小,因此,实际分配的内存空间大小就等于用户申请的内存空间大小加上空闲块头部的大小;最后再加上头部之后,还要对整个大小进行对齐。
下一个 if 判断:
if( ( xWantedSize > 0 ) && ( xWantedSize < configADJUSTED_HEAP_SIZE ) ) | |
{ | |
/* Blocks are stored in byte order - traverse the list from the start | |
(smallest) block until one of adequate size is found. */ | |
pxPreviousBlock = &xStart; | |
pxBlock = xStart.pxNextFreeBlock; | |
while( ( pxBlock->xBlockSize < xWantedSize ) && ( pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock != NULL ) ) | |
{ | |
pxPreviousBlock = pxBlock; | |
pxBlock = pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock; | |
} | |
/* If we found the end marker then a block of adequate size was not found. */ | |
if( pxBlock != &xEnd ) | |
{ | |
/* Return the memory space - jumping over the BlockLink_t structure | |
at its start. */ | |
pvReturn = ( void * ) ( ( ( uint8_t * ) pxPreviousBlock->pxNextFreeBlock ) + heapSTRUCT_SIZE ); | |
/* This block is being returned for use so must be taken out of the | |
list of free blocks. */ | |
pxPreviousBlock->pxNextFreeBlock = pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock; | |
/* If the block is larger than required it can be split into two. */ | |
if( ( pxBlock->xBlockSize - xWantedSize ) > heapMINIMUM_BLOCK_SIZE ) | |
{ | |
/* This block is to be split into two. Create a new block | |
following the number of bytes requested. The void cast is | |
used to prevent byte alignment warnings from the compiler. */ | |
pxNewBlockLink = ( void * ) ( ( ( uint8_t * ) pxBlock ) + xWantedSize ); | |
/* Calculate the sizes of two blocks split from the single | |
block. */ | |
pxNewBlockLink->xBlockSize = pxBlock->xBlockSize - xWantedSize; | |
pxBlock->xBlockSize = xWantedSize; | |
/* Insert the new block into the list of free blocks. */ | |
prvInsertBlockIntoFreeList( ( pxNewBlockLink ) ); | |
} | |
xFreeBytesRemaining -= pxBlock->xBlockSize; | |
} | |
} |
先是判断用户申请的空间大小是否存在(不等于零)以及是否已经超过堆空间大小,若是不符合那就直接 pass 掉了;在这里,块的大小是按从小到大的顺序排列的,因此从一开始遍历列表 (最小的) 块,直到找到一个合适的大小,最后把位置记录下来。
/* If we found the end marker then a block of adequate size was not found. */ | |
if( pxBlock != &xEnd ) | |
{ | |
/* Return the memory space - jumping over the BlockLink_t structure | |
at its start. */ | |
pvReturn = ( void * ) ( ( ( uint8_t * ) pxPreviousBlock->pxNextFreeBlock ) + heapSTRUCT_SIZE ); | |
/* This block is being returned for use so must be taken out of the | |
list of free blocks. */ | |
pxPreviousBlock->pxNextFreeBlock = pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock; | |
/* If the block is larger than required it can be split into two. */ | |
if( ( pxBlock->xBlockSize - xWantedSize ) > heapMINIMUM_BLOCK_SIZE ) | |
{ | |
/* This block is to be split into two. Create a new block | |
following the number of bytes requested. The void cast is | |
used to prevent byte alignment warnings from the compiler. */ | |
pxNewBlockLink = ( void * ) ( ( ( uint8_t * ) pxBlock ) + xWantedSize ); | |
/* Calculate the sizes of two blocks split from the single | |
block. */ | |
pxNewBlockLink->xBlockSize = pxBlock->xBlockSize - xWantedSize; | |
pxBlock->xBlockSize = xWantedSize; | |
/* Insert the new block into the list of free blocks. */ | |
prvInsertBlockIntoFreeList( ( pxNewBlockLink ) ); | |
} | |
xFreeBytesRemaining -= pxBlock->xBlockSize; | |
} |
紧接着,在上面的一段代码里,先是把返回的空间地址值修改(跳过 BlockLink_t 结构),然后把上一个的下一个的节点指向当前下一个的空闲块;后面,若果分配出去的空闲块的剩余空间是比两倍的空闲块头部结构体大小还要大,则将分配出去的这个空闲块分割剩余的空间出来,重新放到空闲块链表中。
值得注意的是 prvInsertBlockIntoFreeList 这个是个宏,具体实现如下:
/* | |
* Insert a block into the list of free blocks - which is ordered by size of | |
* the block. Small blocks at the start of the list and large blocks at the end | |
* of the list. | |
*/ | |
#define prvInsertBlockIntoFreeList( pxBlockToInsert ) \ | |
{ \ | |
BlockLink_t *pxIterator; \ | |
size_t xBlockSize; \ | |
\ | |
xBlockSize = pxBlockToInsert->xBlockSize; \ | |
\ | |
/* Iterate through the list until a block is found that has a larger size */ \ | |
/* than the block we are inserting. */ \ | |
for( pxIterator = &xStart; pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock->xBlockSize < xBlockSize; pxIterator = pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock ) \ | |
{ \ | |
/* There is nothing to do here - just iterate to the correct position. */ \ | |
} \ | |
\ | |
/* Update the list to include the block being inserted in the correct */ \ | |
/* position. */ \ | |
pxBlockToInsert->pxNextFreeBlock = pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock; \ | |
pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock = pxBlockToInsert; \ | |
} |
这个宏的作用就是将新空闲块插入到合适的链表位置中。
后面的代码执行就跟 heap_1 一样了,修改剩余空闲块空闲大小 xFreeBytesRemaining 、恢复所有挂起的任务等等。
3、最后剩下的就是 heap_1 中不支持的 vPortFree() 释放函数了。
void vPortFree( void *pv ) | |
{ | |
uint8_t *puc = ( uint8_t * ) pv; | |
BlockLink_t *pxLink; | |
if( pv != NULL ) | |
{ | |
/* The memory being freed will have an BlockLink_t structure immediately | |
before it. */ | |
puc -= heapSTRUCT_SIZE; | |
/* This unexpected casting is to keep some compilers from issuing | |
byte alignment warnings. */ | |
pxLink = ( void * ) puc; | |
vTaskSuspendAll(); | |
{ | |
/* Add this block to the list of free blocks. */ | |
prvInsertBlockIntoFreeList( ( ( BlockLink_t * ) pxLink ) ); | |
xFreeBytesRemaining += pxLink->xBlockSize; | |
traceFREE( pv, pxLink->xBlockSize ); | |
} | |
( void ) xTaskResumeAll(); | |
} | |
} |
这一个函数炒鸡简单,而且非常短,首先判断要释放的内存是否为空;若是不为空,则获取这个内存空间真正的的空闲块(剔除头部的 BlockLink_t 结构),然后挂起所有任务,把释放的内存重新插入到空闲块链表中,最后调用调试信息宏,恢复挂起的任务就结束了。
特点:
即使应用程序反复删除任务,队列,信号量,互斥量等对象,也可以使用,有关内存碎片的警告如下:
- 如果不是,如果被分配和释放内存使用是随机的大小。例如:
- 如果应用程序以动态创建和删除任务,并且分配给正在创建的任务的堆栈大小始终相同,则在大多数情况下可以使用
heap_2.c;但是,如果分配给正在创建的任务的堆栈大小并不总是相同,则可用的空闲内存可能会分成许多小块,最终导致分配失败;在这种情况下,heap_4.c会更好 - 如果应用程序以动态创建和删除队列,并且每种情况下队列存储区域都相同(队列存储区域指队列项数目乘以每个队列长度),则在大多数情况下都可以使用
heap_2.c;但是,如果队列存储区域在每种情况下都不相同,则可用的空闲内存可能会分成许多小块,最终导致分配失败;在这种情况下,heap_4.c会更好 - 该应用程序直接调用
pvPortMalloc()和vPortFree(),而不仅仅是通过其他 FreeRTOS API 函数间接调用。
- 如果应用程序以动态创建和删除任务,并且分配给正在创建的任务的堆栈大小始终相同,则在大多数情况下可以使用
- 如果您的应用程序的队列,任务,信号量,互斥量等处于以不可预测的顺序,则可能会导致内存碎片问题;虽然这是小概率事件,但应牢记。
- 不确定型,但比大多数标准 C 库
malloc实现要有效得多。
# heap_3.c
heap_3.c 就更简单了,只是简单的包装一下标准函数 malloc() 和 free() 以确保线程安全,在大多数情况下,这些包装器将需要你的编译器提供,它们依赖于编译器自己的 malloc() 和 free() 实现;文件说明如下: Implementation of pvPortMalloc() and vPortFree() that relies on the compilers own malloc() and free() implementations.This file can only be used if the linker is configured to to generate a heap memory area.
1、封装 malloc()
void *pvPortMalloc( size_t xWantedSize ) | |
{ | |
void *pvReturn; | |
vTaskSuspendAll(); | |
{ | |
pvReturn = malloc( xWantedSize ); | |
traceMALLOC( pvReturn, xWantedSize ); | |
} | |
( void ) xTaskResumeAll(); | |
#if( configUSE_MALLOC_FAILED_HOOK == 1 ) | |
{ | |
if( pvReturn == NULL ) | |
{ | |
extern void vApplicationMallocFailedHook( void ); | |
vApplicationMallocFailedHook(); | |
} | |
} | |
#endif | |
return pvReturn; | |
} |
和 heap_1 、 heap_2 一样,用 vTaskSuspendAll() 挂起所有的任务,以确保分配内存的过程是线程安全的;随后才使用 malloc() 进行内存分配,记录内存地址;然后就是调用调试信息宏 traceMALLOC() ,最后调用 xTaskResumeAll() 恢复所有被挂起的任务;如果在 FreeRTOS.h 中使能了勾子函数宏 configUSE_MALLOC_FAILED_HOOK ,则在调用勾子函数 vApplicationMallocFailedHook() 之后再向用户返回分配内存的首地址。
2、封装 free()
void vPortFree( void *pv ) | |
{ | |
if( pv ) | |
{ | |
vTaskSuspendAll(); | |
{ | |
free( pv ); | |
traceFREE( pv, 0 ); | |
} | |
( void ) xTaskResumeAll(); | |
} | |
} |
一样的,检查指针的有效性、挂起全部任务、调用 free() 接口将内存回收、调用调试信息宏、恢复挂起的任务,然后就没了。
此实现方法及特点:
- 需要链接器设置堆,并且需要编译器库提供
malloc()和free()实现。 - 具有不确定性。
- 可能会大大增加 RTOS 内核代码的大小。
注意,当使用 heap_3 时, FreeRTOSConfig.h 中的宏 configTOTAL_HEAP_SIZE 设置无效。
# heap_4.c
跟方案 2 不一样的是,这个方案使用了首次适应算法(first fit algorithm);它会将相邻的空闲内存块合并成一个更大的块(包含一个合并算法)。
具体是它们会在释放时合并相邻的内存块,从而限制内存碎片,文件中的注释也有说: A sample implementation of pvPortMalloc() and vPortFree() that combines (coalescences) adjacent memory blocks as they are freed, and in so doing limits memory fragmentation.
其实, heap_4 的代码基本跟 heap_2 的代码实现差不多,只不过增加了些功能(合并算法),而且你别看他代码太长,其实有很多东西都没用到的,就像这个函数 mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER() ,其实他是个宏,但是他并没有实现什么,根据他的命名可以认定为只是作者预留的一个调试输出窗口而已;还有 configASSERT() 这个也是一个宏,也只是用来调试输出而已,具体配置修改看下一篇。
1、没错,还是我们首要分析的初始化函数。
static void prvHeapInit( void ) | |
{ | |
BlockLink_t *pxFirstFreeBlock; | |
uint8_t *pucAlignedHeap; | |
size_t uxAddress; | |
size_t xTotalHeapSize = configTOTAL_HEAP_SIZE; | |
/* Ensure the heap starts on a correctly aligned boundary. */ | |
uxAddress = ( size_t ) ucHeap; | |
if( ( uxAddress & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) != 0 ) | |
{ | |
uxAddress += ( portBYTE_ALIGNMENT - 1 ); | |
uxAddress &= ~( ( size_t ) portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ); | |
xTotalHeapSize -= uxAddress - ( size_t ) ucHeap; | |
} | |
pucAlignedHeap = ( uint8_t * ) uxAddress; | |
/* xStart is used to hold a pointer to the first item in the list of free | |
blocks. The void cast is used to prevent compiler warnings. */ | |
xStart.pxNextFreeBlock = ( void * ) pucAlignedHeap; | |
xStart.xBlockSize = ( size_t ) 0; | |
/* pxEnd is used to mark the end of the list of free blocks and is inserted | |
at the end of the heap space. */ | |
uxAddress = ( ( size_t ) pucAlignedHeap ) + xTotalHeapSize; | |
uxAddress -= xHeapStructSize; | |
uxAddress &= ~( ( size_t ) portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ); | |
pxEnd = ( void * ) uxAddress; | |
pxEnd->xBlockSize = 0; | |
pxEnd->pxNextFreeBlock = NULL; | |
/* To start with there is a single free block that is sized to take up the | |
entire heap space, minus the space taken by pxEnd. */ | |
pxFirstFreeBlock = ( void * ) pucAlignedHeap; | |
pxFirstFreeBlock->xBlockSize = uxAddress - ( size_t ) pxFirstFreeBlock; | |
pxFirstFreeBlock->pxNextFreeBlock = pxEnd; | |
/* Only one block exists - and it covers the entire usable heap space. */ | |
xMinimumEverFreeBytesRemaining = pxFirstFreeBlock->xBlockSize; | |
xFreeBytesRemaining = pxFirstFreeBlock->xBlockSize; | |
/* Work out the position of the top bit in a size_t variable. */ | |
xBlockAllocatedBit = ( ( size_t ) 1 ) << ( ( sizeof( size_t ) * heapBITS_PER_BYTE ) - 1 ); | |
} |
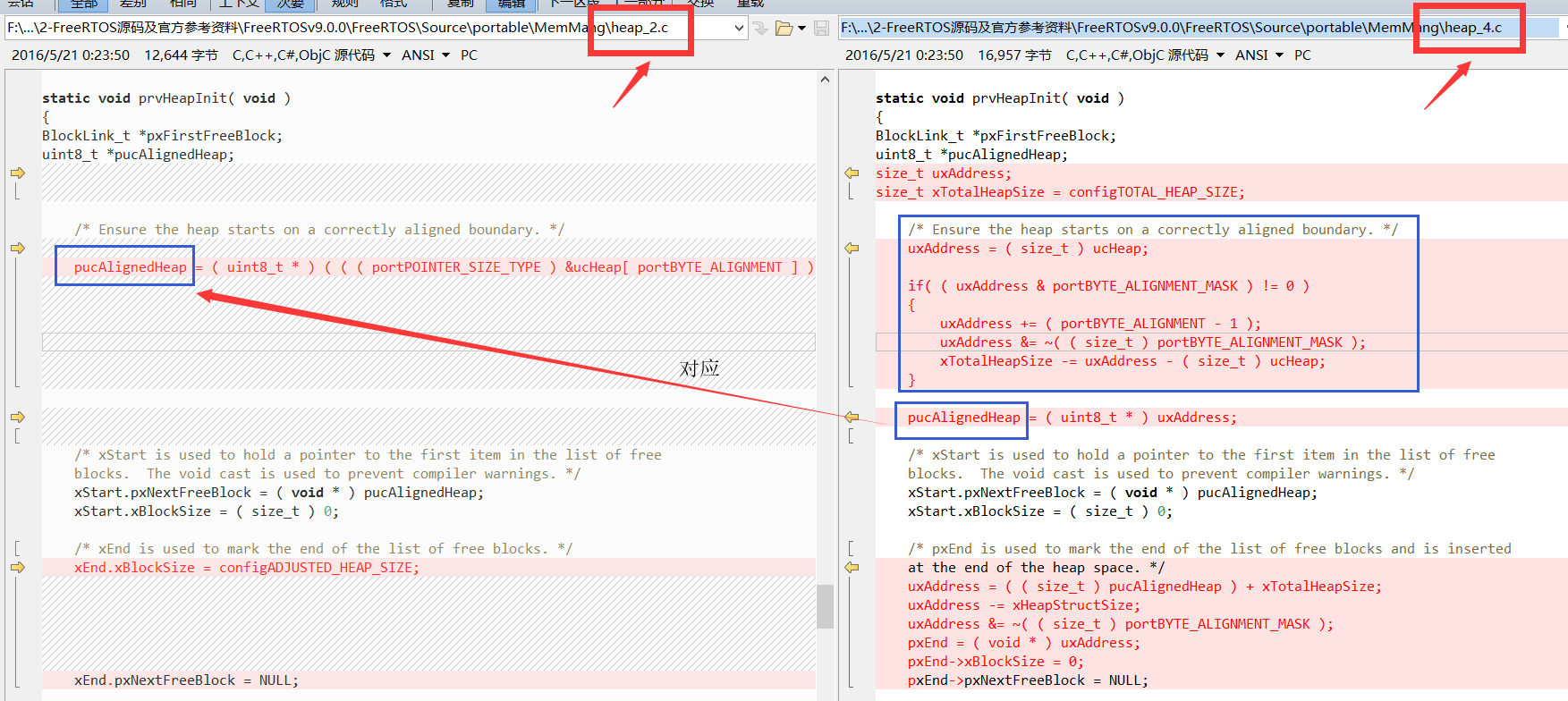
根据上图现在来对比一下 head_2 的,这里对起始地址做字节对齐处理是跟 head_2 有点不同,他不止对内存堆进行首地址对齐保存 pucAlignedHeap ,并且还算出可用空间大小为 xTotalHeapSize ;
然后, xStart 的初始化是一样的,没什么好说的,注意 xStart 是 BlockLink_t 的一个实体变量,存储在静态存储区;
接着是 pxEnd ,他是一个 BlockLink_t 的指针,存储在静态存储区中,却指向了内存堆的最后一个 BlockLink_t 大小的位置上。也就是说,内存堆最后的空间是存储着一个 BlockLink_t ,用来指示空闲块链表的最后位置,这是和 heap_2 所不同的地方:
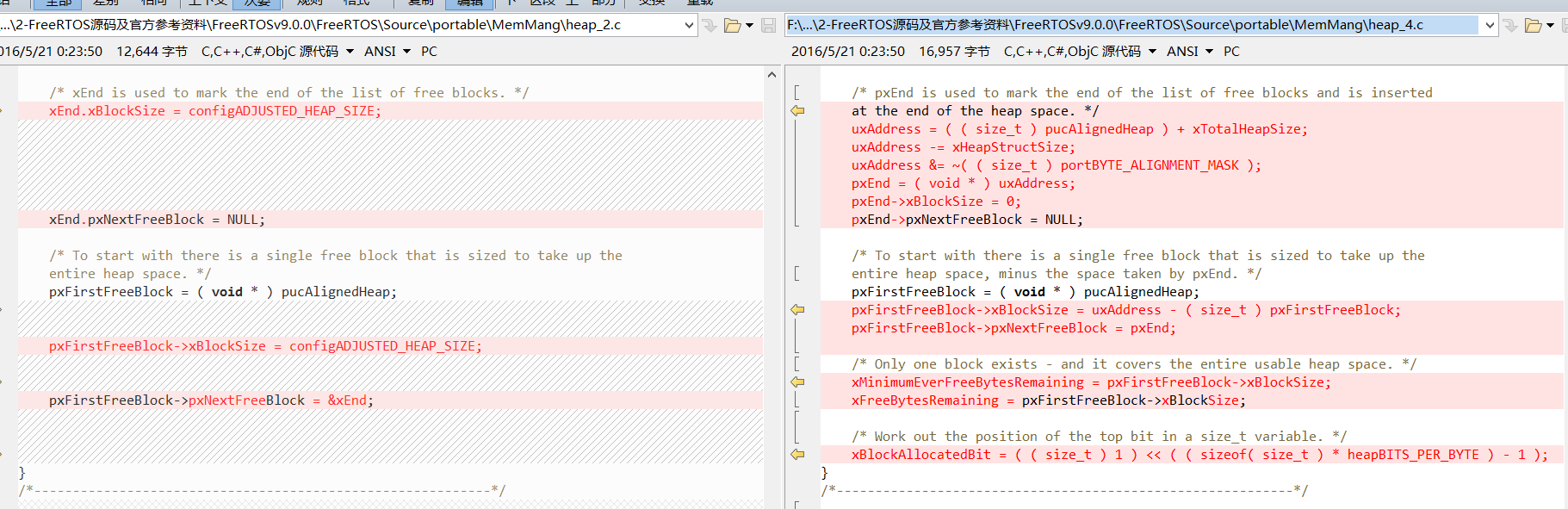
因为 pxEnd 占用了一个 BlockLink_t 大小的空间,所以在整个堆空间,减去 pxEnd 占用的空间;
另外,为了安全, heap_4 增加一个位( BlockLink_t 中 xBlockSize 的最高位)标记某个内存块是否处于空闲状态,因此在初始化的时候设置 xBlockAllocatedBit 的值。
2、在对比分析 pvPortMalloc() 内存分布的实现之前,我们先分析一下 prvInsertBlockIntoFreeList() 函数。
static void prvInsertBlockIntoFreeList( BlockLink_t *pxBlockToInsert ) | |
{ | |
BlockLink_t *pxIterator; | |
uint8_t *puc; | |
/* Iterate through the list until a block is found that has a higher address | |
than the block being inserted. */ | |
for( pxIterator = &xStart; pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock < pxBlockToInsert; pxIterator = pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock ) | |
{ | |
/* Nothing to do here, just iterate to the right position. */ | |
} | |
/* Do the block being inserted, and the block it is being inserted after | |
make a contiguous block of memory? */ | |
puc = ( uint8_t * ) pxIterator; | |
if( ( puc + pxIterator->xBlockSize ) == ( uint8_t * ) pxBlockToInsert ) | |
{ | |
pxIterator->xBlockSize += pxBlockToInsert->xBlockSize; | |
pxBlockToInsert = pxIterator; | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); | |
} | |
/* Do the block being inserted, and the block it is being inserted before | |
make a contiguous block of memory? */ | |
puc = ( uint8_t * ) pxBlockToInsert; | |
if( ( puc + pxBlockToInsert->xBlockSize ) == ( uint8_t * ) pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock ) | |
{ | |
if( pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock != pxEnd ) | |
{ | |
/* Form one big block from the two blocks. */ | |
pxBlockToInsert->xBlockSize += pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock->xBlockSize; | |
pxBlockToInsert->pxNextFreeBlock = pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock->pxNextFreeBlock; | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
pxBlockToInsert->pxNextFreeBlock = pxEnd; | |
} | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
pxBlockToInsert->pxNextFreeBlock = pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock; | |
} | |
/* If the block being inserted plugged a gab, so was merged with the block | |
before and the block after, then it's pxNextFreeBlock pointer will have | |
already been set, and should not be set here as that would make it point | |
to itself. */ | |
if( pxIterator != pxBlockToInsert ) | |
{ | |
pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock = pxBlockToInsert; | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); | |
} | |
} |
这个函数就是合并实现的主要环节了;在 heap_2 中的链表插入是通过宏实现的,并且是按内存块大小进行插入;而 heap_4 的插入操作是写成了一个函数,该函数按内存块地址进行插入(低位前),实际上是将这个空闲块链表里的所有空闲块按地址顺序排列,这么做是为了实现内存块合并;前面也说了,相对于 heap_2 , heap_4 会将相邻的空闲内存块合并成一个更大的块,若果不这么排列,那么就不能将相邻的空闲块进行合并了。
首先,通过一次链表的遍历,找出内存块插入点(把 pxIterator 找出来);然后判断,正在插入的块( pxBlockToInsert )和内存块插入点( pxIterator )是否构成一个连续的内存块;其标准为 pxIterator 的首地址加上 pxIterator 的块大小之后等于 pxBlockToInsert 的首地址,相等就说明两个块是相邻的,把这个待插入的空闲块插到 pxIterator 的后面,否则就什么事都不做。
/* Iterate through the list until a block is found that has a higher address | |
than the block being inserted. */ | |
for( pxIterator = &xStart; pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock < pxBlockToInsert; pxIterator = pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock ) | |
{ | |
/* Nothing to do here, just iterate to the right position. */ | |
} | |
/* Do the block being inserted, and the block it is being inserted after | |
make a contiguous block of memory? */ | |
puc = ( uint8_t * ) pxIterator; | |
if( ( puc + pxIterator->xBlockSize ) == ( uint8_t * ) pxBlockToInsert ) | |
{ | |
pxIterator->xBlockSize += pxBlockToInsert->xBlockSize; | |
pxBlockToInsert = pxIterator; | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); | |
} |
然后,再试着将 pxBlockToInsert 和 pxIterator 指向的下一个空闲块进行合并;这次用 pxBlockToInsert 的首地址加上 pxBlockToInsert 的块大小与 pxIterator 指向的下一个块地址比较,不符合,则要修改 pxBlockToInsert 的 Next 指针,指向 pxIterator 的下一个空闲块;如果符合条件,则再判断 pxIterator 指向的下一个块地址是否已经到了空闲块链表的最后位置了,如果已经到了空闲块链表的最后位置,那么就把 pxIterator 指向的下一个块地址更改为空闲块链表的最后位置的地址,否则就合并内存并且更新链表的数据。
/* Do the block being inserted, and the block it is being inserted before | |
make a contiguous block of memory? */ | |
puc = ( uint8_t * ) pxBlockToInsert; | |
if( ( puc + pxBlockToInsert->xBlockSize ) == ( uint8_t * ) pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock ) | |
{ | |
if( pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock != pxEnd ) | |
{ | |
/* Form one big block from the two blocks. */ | |
pxBlockToInsert->xBlockSize += pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock->xBlockSize; | |
pxBlockToInsert->pxNextFreeBlock = pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock->pxNextFreeBlock; | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
pxBlockToInsert->pxNextFreeBlock = pxEnd; | |
} | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
pxBlockToInsert->pxNextFreeBlock = pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock; | |
} |
最后,要是 pxBlockToInsert 没有和 pxIterator 合并,则还要修改 pxIterator 的 Next 指针。
/* If the block being inserted plugged a gab, so was merged with the block | |
before and the block after, then it's pxNextFreeBlock pointer will have | |
already been set, and should not be set here as that would make it point | |
to itself. */ | |
if( pxIterator != pxBlockToInsert ) | |
{ | |
pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock = pxBlockToInsert; | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); | |
} |
3、讲了这么多,现在终于到分析 pvPortMalloc() 了。
先看总代码:
void *pvPortMalloc( size_t xWantedSize ) | |
{ | |
BlockLink_t *pxBlock, *pxPreviousBlock, *pxNewBlockLink; | |
void *pvReturn = NULL; | |
vTaskSuspendAll(); | |
{ | |
/* If this is the first call to malloc then the heap will require | |
initialisation to setup the list of free blocks. */ | |
if( pxEnd == NULL ) | |
{ | |
prvHeapInit(); | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); | |
} | |
/* Check the requested block size is not so large that the top bit is | |
set. The top bit of the block size member of the BlockLink_t structure | |
is used to determine who owns the block - the application or the | |
kernel, so it must be free. */ | |
if( ( xWantedSize & xBlockAllocatedBit ) == 0 ) | |
{ | |
/* The wanted size is increased so it can contain a BlockLink_t | |
structure in addition to the requested amount of bytes. */ | |
if( xWantedSize > 0 ) | |
{ | |
xWantedSize += xHeapStructSize; | |
/* Ensure that blocks are always aligned to the required number | |
of bytes. */ | |
if( ( xWantedSize & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) != 0x00 ) | |
{ | |
/* Byte alignment required. */ | |
xWantedSize += ( portBYTE_ALIGNMENT - ( xWantedSize & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) ); | |
configASSERT( ( xWantedSize & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) == 0 ); | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); | |
} | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); | |
} | |
if( ( xWantedSize > 0 ) && ( xWantedSize <= xFreeBytesRemaining ) ) | |
{ | |
/* Traverse the list from the start (lowest address) block until | |
one of adequate size is found. */ | |
pxPreviousBlock = &xStart; | |
pxBlock = xStart.pxNextFreeBlock; | |
while( ( pxBlock->xBlockSize < xWantedSize ) && ( pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock != NULL ) ) | |
{ | |
pxPreviousBlock = pxBlock; | |
pxBlock = pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock; | |
} | |
/* If the end marker was reached then a block of adequate size | |
was not found. */ | |
if( pxBlock != pxEnd ) | |
{ | |
/* Return the memory space pointed to - jumping over the | |
BlockLink_t structure at its start. */ | |
pvReturn = ( void * ) ( ( ( uint8_t * ) pxPreviousBlock->pxNextFreeBlock ) + xHeapStructSize ); | |
/* This block is being returned for use so must be taken out | |
of the list of free blocks. */ | |
pxPreviousBlock->pxNextFreeBlock = pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock; | |
/* If the block is larger than required it can be split into | |
two. */ | |
if( ( pxBlock->xBlockSize - xWantedSize ) > heapMINIMUM_BLOCK_SIZE ) | |
{ | |
/* This block is to be split into two. Create a new | |
block following the number of bytes requested. The void | |
cast is used to prevent byte alignment warnings from the | |
compiler. */ | |
pxNewBlockLink = ( void * ) ( ( ( uint8_t * ) pxBlock ) + xWantedSize ); | |
configASSERT( ( ( ( size_t ) pxNewBlockLink ) & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) == 0 ); | |
/* Calculate the sizes of two blocks split from the | |
single block. */ | |
pxNewBlockLink->xBlockSize = pxBlock->xBlockSize - xWantedSize; | |
pxBlock->xBlockSize = xWantedSize; | |
/* Insert the new block into the list of free blocks. */ | |
prvInsertBlockIntoFreeList( pxNewBlockLink ); | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); | |
} | |
xFreeBytesRemaining -= pxBlock->xBlockSize; | |
if( xFreeBytesRemaining < xMinimumEverFreeBytesRemaining ) | |
{ | |
xMinimumEverFreeBytesRemaining = xFreeBytesRemaining; | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); | |
} | |
/* The block is being returned - it is allocated and owned | |
by the application and has no "next" block. */ | |
pxBlock->xBlockSize |= xBlockAllocatedBit; | |
pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock = NULL; | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); | |
} | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); | |
} | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); | |
} | |
traceMALLOC( pvReturn, xWantedSize ); | |
} | |
( void ) xTaskResumeAll(); | |
#if( configUSE_MALLOC_FAILED_HOOK == 1 ) | |
{ | |
if( pvReturn == NULL ) | |
{ | |
extern void vApplicationMallocFailedHook( void ); | |
vApplicationMallocFailedHook(); | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); | |
} | |
} | |
#endif | |
configASSERT( ( ( ( size_t ) pvReturn ) & ( size_t ) portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) == 0 ); | |
return pvReturn; | |
} |
其实相对于 heap_2 的变动不大,可以看一下它们的对比图:
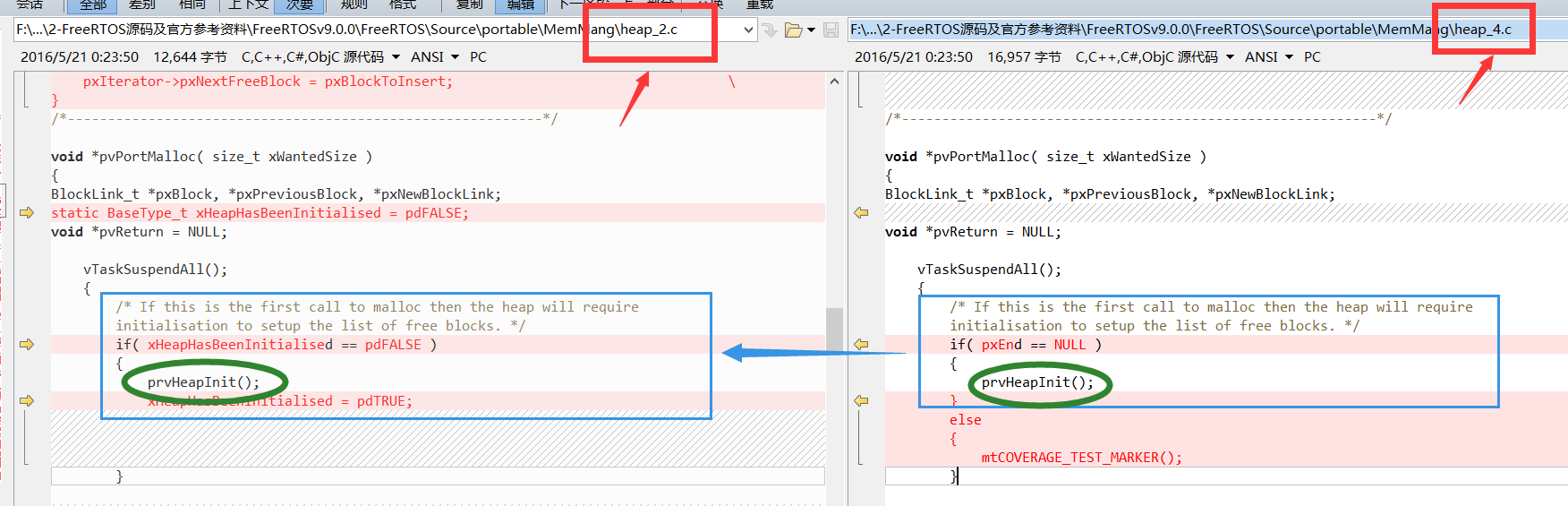
同样的,只在第一次调用该函数的时候才初始化堆管理,看上图。
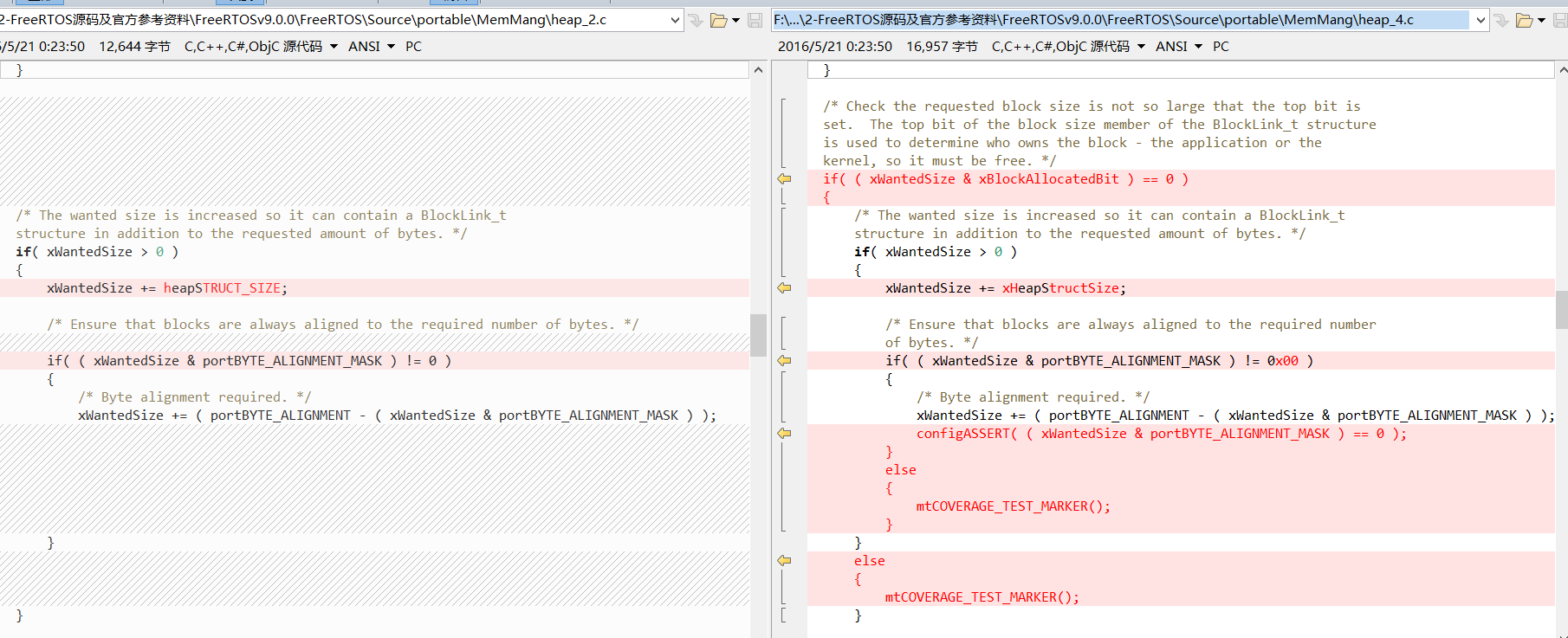
接着在这里只是相对于 heap_2 多了个标志位 xBlockAllocatedBit 的判断来是否执行以下的操作,若是符合,则像 heap_2 一样进行块字节对齐,看上图。
而剩下的,主要的不同也就是因为多了个 xBlockAllocatedBit 操作,所以使用了 xBlockSize 的最高位做标记,因此就添加了相应的操作,如下图:
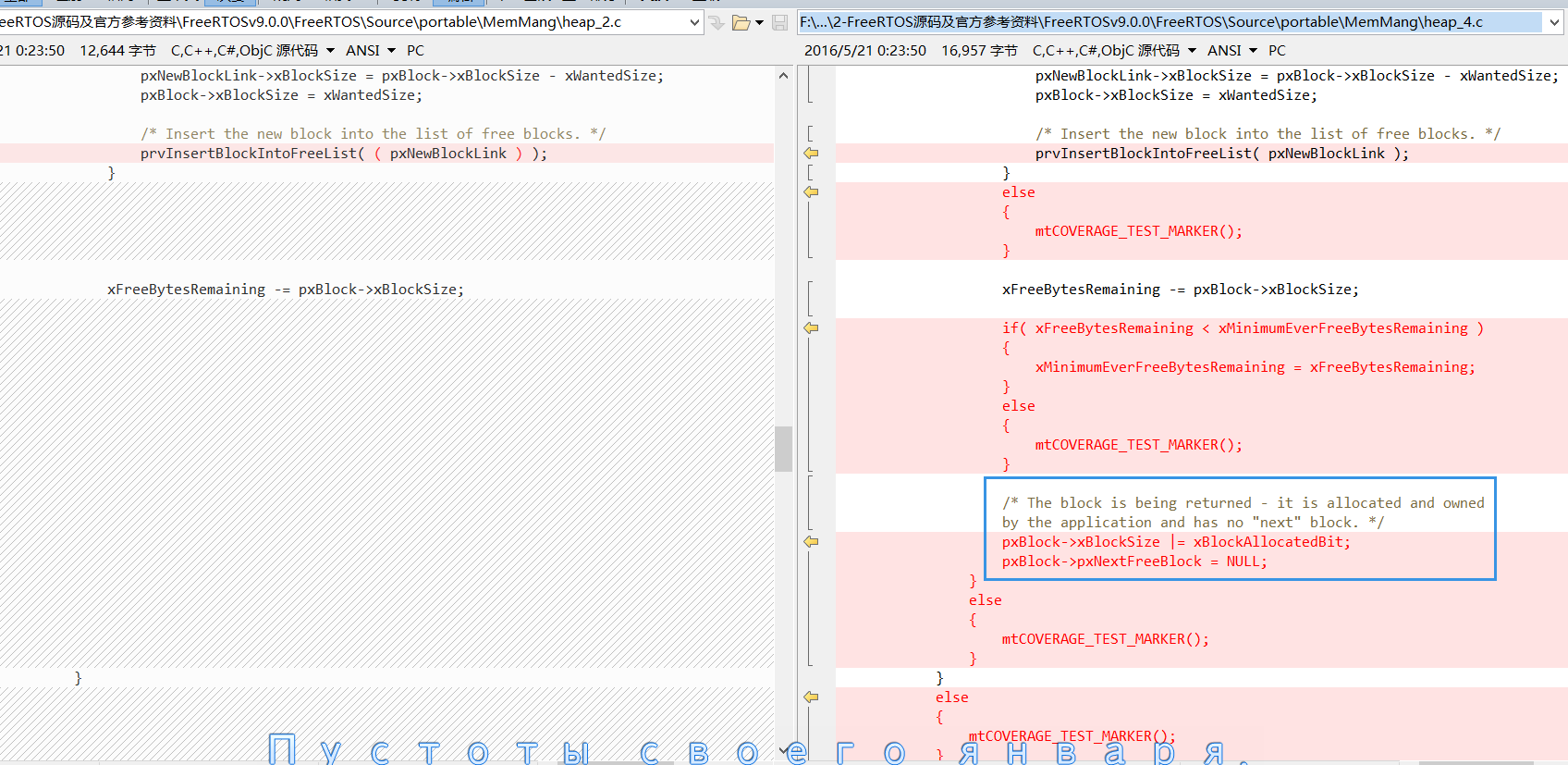
至于其他差别不大,此处不做赘述。
4、 vPortFree() 实现
void vPortFree( void *pv ) | |
{ | |
uint8_t *puc = ( uint8_t * ) pv; | |
BlockLink_t *pxLink; | |
if( pv != NULL ) | |
{ | |
/* The memory being freed will have an BlockLink_t structure immediately | |
before it. */ | |
puc -= xHeapStructSize; | |
/* This casting is to keep the compiler from issuing warnings. */ | |
pxLink = ( void * ) puc; | |
/* Check the block is actually allocated. */ | |
configASSERT( ( pxLink->xBlockSize & xBlockAllocatedBit ) != 0 ); | |
configASSERT( pxLink->pxNextFreeBlock == NULL ); | |
if( ( pxLink->xBlockSize & xBlockAllocatedBit ) != 0 ) | |
{ | |
if( pxLink->pxNextFreeBlock == NULL ) | |
{ | |
/* The block is being returned to the heap - it is no longer | |
allocated. */ | |
pxLink->xBlockSize &= ~xBlockAllocatedBit; | |
vTaskSuspendAll(); | |
{ | |
/* Add this block to the list of free blocks. */ | |
xFreeBytesRemaining += pxLink->xBlockSize; | |
traceFREE( pv, pxLink->xBlockSize ); | |
prvInsertBlockIntoFreeList( ( ( BlockLink_t * ) pxLink ) ); | |
} | |
( void ) xTaskResumeAll(); | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); | |
} | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER(); | |
} | |
} | |
} |
相比 heap_2 , heap_4 只是多了一些检查,使之更加安全,看下图比较:
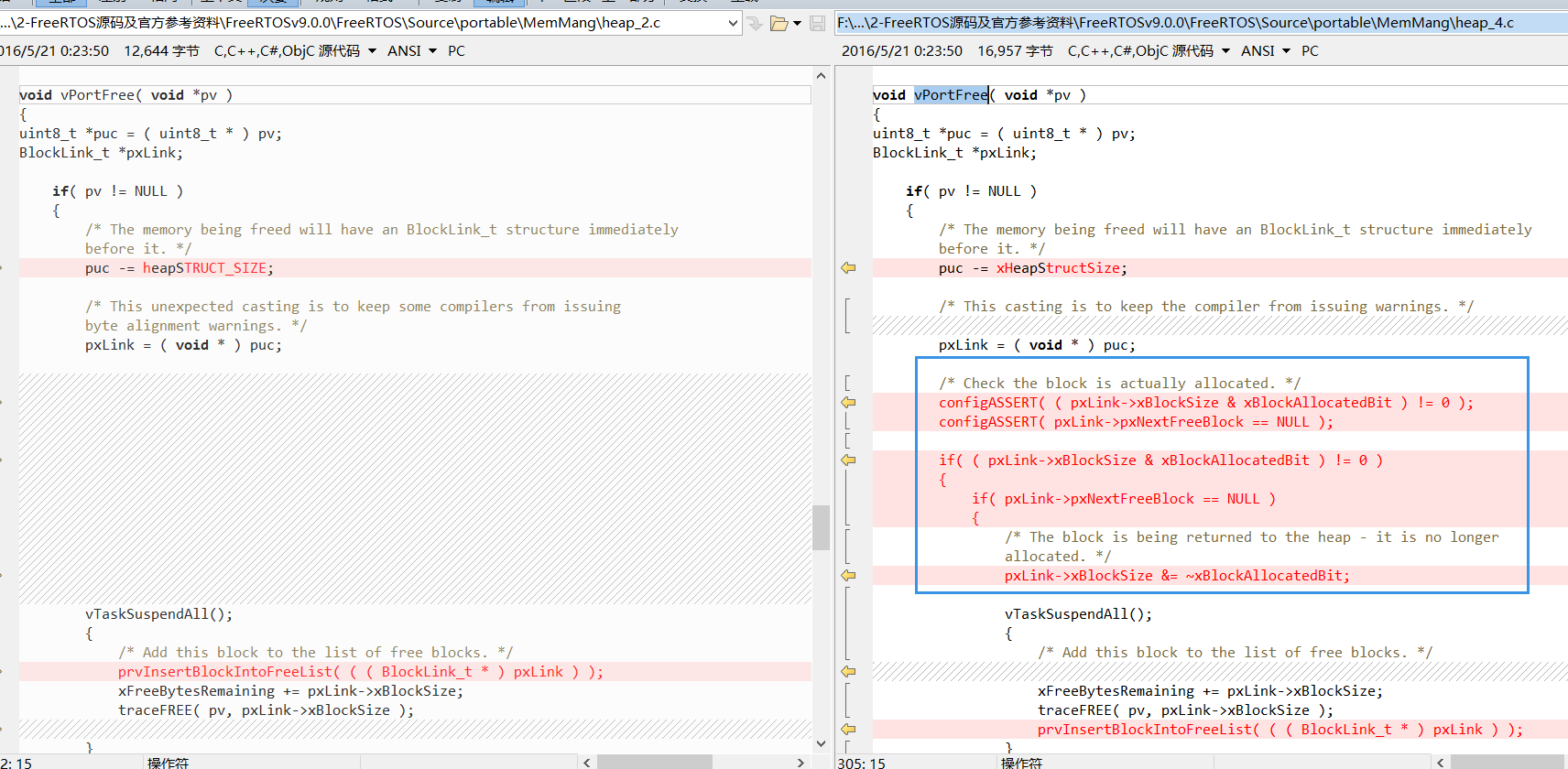
应用场景及特点:
- 即使应用程序反复删除任务,队列,信号量,互斥量等也可以使用。
- 与
heap_2实现相比,即使将要分配和释放的内存具有随机大小,也很难将堆空间严重分割成多个小块。 - 不确定性,但比大多数标准 C 库
malloc实现要有效得多。
对于希望直接在应用程序代码中使用便携式层内存分配方案的应用程序, heap_4.c 尤其有用(而不是仅通过调用本身调用 pvPortMalloc() 和 vPortFree() 的 API 函数来间接使用)。
# heap_5.c
该方案使用与 heap_4 相同,使用首次适应算法和内存合并算法,并允许堆跨越多个不相邻(不连续)的内存区域。
这个就不说了,跟 heap_4 大同小异,有兴趣可以看看,就只发一下它的文件注释说明吧
/* | |
* A sample implementation of pvPortMalloc() that allows the heap to be defined | |
* across multiple non-contigous blocks and combines (coalescences) adjacent | |
* memory blocks as they are freed. | |
* | |
* See heap_1.c, heap_2.c, heap_3.c and heap_4.c for alternative | |
* implementations, and the memory management pages of http://www.FreeRTOS.org | |
* for more information. | |
* | |
* Usage notes: | |
* | |
* vPortDefineHeapRegions() ***must*** be called before pvPortMalloc(). | |
* pvPortMalloc() will be called if any task objects (tasks, queues, event | |
* groups, etc.) are created, therefore vPortDefineHeapRegions() ***must*** be | |
* called before any other objects are defined. | |
* | |
* vPortDefineHeapRegions() takes a single parameter. The parameter is an array | |
* of HeapRegion_t structures. HeapRegion_t is defined in portable.h as | |
* | |
* typedef struct HeapRegion | |
* { | |
* uint8_t *pucStartAddress; << Start address of a block of memory that will be part of the heap. | |
* size_t xSizeInBytes; << Size of the block of memory. | |
* } HeapRegion_t; | |
* | |
* The array is terminated using a NULL zero sized region definition, and the | |
* memory regions defined in the array ***must*** appear in address order from | |
* low address to high address. So the following is a valid example of how | |
* to use the function. | |
* | |
* HeapRegion_t xHeapRegions[] = | |
* { | |
* { ( uint8_t * ) 0x80000000UL, 0x10000 }, << Defines a block of 0x10000 bytes starting at address 0x80000000 | |
* { ( uint8_t * ) 0x90000000UL, 0xa0000 }, << Defines a block of 0xa0000 bytes starting at address of 0x90000000 | |
* { NULL, 0 } << Terminates the array. | |
* }; | |
* | |
* vPortDefineHeapRegions( xHeapRegions ); << Pass the array into vPortDefineHeapRegions(). | |
* | |
* Note 0x80000000 is the lower address so appears in the array first. | |
* | |
*/ |
注意: heap_5 通过调用 vPortDefineHeapRegions() 函数实现初始化,只有在 vPortDefineHeapRegions() 执行后才允许使用内存分配和释放。创建 RTOS 对象(任务、队列、信号量等等)会隐含的调用 pvPortMalloc() ,因此必须注意:使用 heap_5 创建任何对象前,要先执行 vPortDefineHeapRegions() 函数。
# 其他
必须吐槽一下,终于结束了。
官方的这个地址有详细说 heap 堆内存管理
然后想要了解 heap 所用到的算法可以查看 -> 分区分配算法(Partitioning Placement Algorithm)